Samrat Roy
A Bayesian Nonparametric Approach for Causal Inference with Multiple Mediators
Abstract
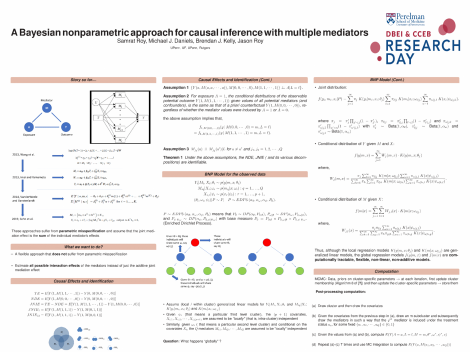
Mediation analysis with contemporaneously observed multiple mediators is a significant area of causal inference. Recent methodologies dealing with multiple mediators are based on parametric models and thus may suffer from parametric misspecification. Also, the existing literature estimates the joint mediation effect as the sum of individual mediators effect, which, on many occasions, is not a reasonable assumption. In this paper, we propose a methodology that overcomes the two aforementioned drawbacks in the existing literature. Our method is based on a novel Bayesian nonparametric (BNP) approach, wherein, the joint distribution of the observed data (outcome, mediators, treatment, and confounders) is modeled flexibly using an enriched Dirichlet process with three levels: the first level characterizing the conditional distribution of the outcome given the mediators, treatment and the confounders, the second level corresponding to the conditional distribution of each of the mediators given the treatment and the confounders, and the third level corresponding to the distribution of the treatment and the confounders. Using the joint distribution in the EDP, we use standardization (g-computation) to compute causal mediation effects. The efficacy of our proposed method is demonstrated with simulations. Also, we apply our proposed method to analyze data from a study of Ventilator-associated Pneumonia (VAP) co-infected patients, where the effect of the abundance of Pseudomonas on VAP infection is suspected to be mediated through various antibiotic exposures.
Keywords
Bayesian nonparametric, Enriched Dirichlet Process, Multiple mediatorsAbout Us
To understand health and disease today, we need new thinking and novel science —the kind we create when multiple disciplines work together from the ground up. That is why this department has put forward a bold vision in population-health science: a single academic home for biostatistics, epidemiology and informatics.
© 2023 Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania. All rights reserved.. | Disclaimer