Vivek Sriram
NETMAGE: A Human-Disease Phenotype Map Generator for the Visualization of PheWAS
Abstract
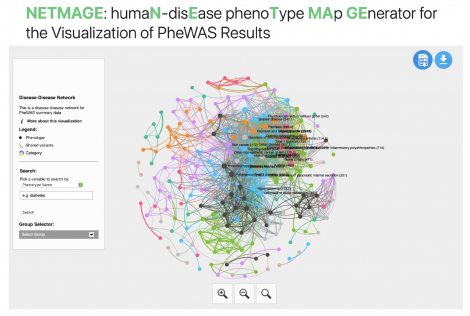
Disease complications, the onset of secondary phenotypes given a primary condition, can exacerbate the long-term severity of outcomes. However, the exact cause of many of these cross-phenotype associations is still unknown. One potential reason is shared genetic etiology—common genetic drivers may lead to the onset of multiple phenotypes. Disease-disease networks (DDNs), where nodes represent diseases and edges represent associations between diseases, can provide an intuitive way of understanding the relationships between phenotypes. Using summary statistics from a phenome-wide association study (PheWAS), we can generate a corresponding DDN where edges represent shared genetic variants between diseases. Such a network can help us analyze genetic associations across the diseasome, the landscape of all human diseases, and identify potential genetic influences for disease complications. To improve the ease of network-based analysis of shared genetic components across phenotypes, we developed the humaN disEase phenoType MAp GEnerator (NETMAGE), a web-based tool that produces interactive DDN visualizations from PheWAS summary statistics. Users can search the map by various attributes and select nodes to view related phenotypes, associated variants, and various network statistics. As a test case, we used NETMAGE to construct a network from UK BioBank (UKBB) PheWAS summary statistic data. Our map correctly displayed previously identified disease comorbidities from the UKBB and identified concentrations of hub diseases in the endocrine/metabolic and circulatory disease categories. By examining the associations between phenotypes in our map, we can identify potential genetic explanations for the relationships between diseases and better understand the underlying architecture of the human diseasome. Our tool thus provides researchers with a means to identify prospective genetic targets for drug design, using network medicine to contribute to the exploration of personalized medicine.
Keywords
Disease-Disease Network, PheWAS, Comorbidity, Disease Complication, Network MedicineAbout Us
To understand health and disease today, we need new thinking and novel science —the kind we create when multiple disciplines work together from the ground up. That is why this department has put forward a bold vision in population-health science: a single academic home for biostatistics, epidemiology and informatics.
© 2023 Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania. All rights reserved.. | Disclaimer


Comments